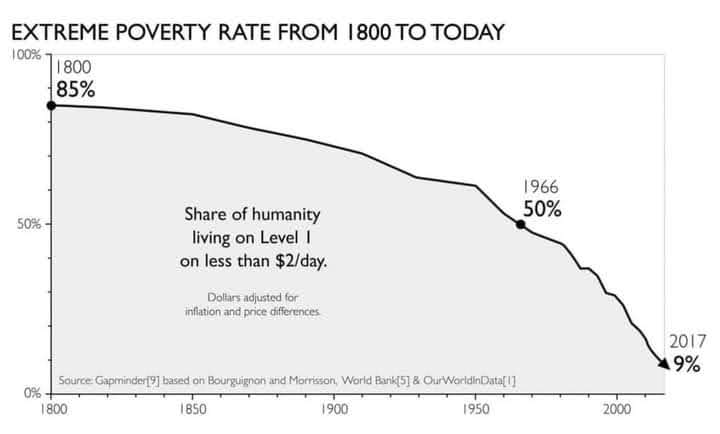
Over the past two centuries, the world has witnessed a remarkable transformation in the realm of economic development and poverty reduction. The proliferation of free-market principles, driven by factors such as globalization and technological advancements, has played a pivotal role in lifting billions of people out of extreme poverty. From a staggering 85% of the global population living in extreme poverty in 1800 to a historic low of 9% in 2017, this article explores how the adoption of free-market principles has catalyzed this dramatic positive change.
The Rise of Free Markets
The 18th and 19th centuries marked the rise of the Industrial Revolution, which saw the emergence of free-market capitalism in various parts of the world. The principles of individual liberty, private property rights, and voluntary exchange gained prominence, empowering individuals to pursue economic opportunities with limited government interference. The idea that individuals should be free to own and manage their resources and engage in trade based on mutual consent fostered innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
Economic Growth and Innovation
The free-market approach paved the way for significant economic growth and technological innovation. Industries expanded, new products and services were introduced, and labor markets diversified. This growth created jobs, improved living standards, and generated wealth that could be reinvested for further development. As competition flourished, industries evolved to meet consumer demands, driving improvements in product quality, affordability, and accessibility.
Globalization and Access to Markets
The increasing interconnectedness of the world through trade and communication fueled the expansion of markets. Globalization enabled countries to specialize in producing goods and services in which they held a comparative advantage, leading to mutually beneficial exchanges and enhanced efficiency. This dynamic spurred economic development in previously marginalized regions, resulting in greater income opportunities and improved quality of life for millions.
Empowering Individuals and Communities
Free-market principles have empowered individuals to break the cycle of poverty by offering them the tools to create economic opportunities. Entrepreneurs can harness their talents, skills, and resources to establish businesses and provide employment. This empowerment, in turn, fosters economic self-sufficiency, social mobility, and the capacity to invest in education and healthcare, further elevating living standards.
Challenges and Ongoing Efforts
While the proliferation of free-market principles has significantly reduced extreme poverty, challenges persist. Income inequality, regional disparities, and access to basic services remain concerns in many parts of the world. Addressing these challenges requires a multidimensional approach, including targeted policies to ensure equitable access to education, healthcare, and social safety nets.
Conclusion
The global reduction of extreme poverty from 85% to 9% over the past two centuries underscores the transformative power of free-market principles. The embrace of individual liberty, entrepreneurship, and voluntary exchange has enabled billions to escape the shackles of poverty and envision brighter futures. While challenges remain, the success story of poverty reduction through free markets serves as a testament to the potential of economic empowerment and the continued pursuit of human progress on a global scale.
 The Libertarian Catholic
The Libertarian Catholic